A terminal emulator is an application that displays a window which allows you to use HP-UX commands and cut and paste text within or between terminal emulation windows.
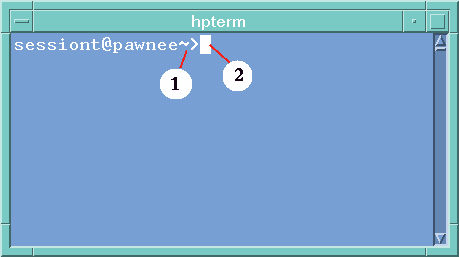
The command line prompt is a special character that is displayed in your terminal emulator after you press Return. It can be a %, $ or other special character. A small box, called a cursor, shows where characters will appear in the window when you type something on the keyboard.

HP VUE provides two terminal emulators:
You can start a HP VUE terminal emulator either with a Front Panel control, from the Toolbox, or by typing a command. The method of stopping the terminal emulator is the same, regardless of how it was started.
A terminal window containing a command line prompt and cursor appears. The terminal emulator that appears is the default terminal emulator.
This opens a Terminal Emulator with the same current working directory as the File Manager view where it is started.
At the command line prompt, type the name of the terminal emulator and any options you want, using:
hpterm [options] &Or:
xterm [options] &Where:
The terminal emulator starts in the current workspace unless directed otherwise by options.
exit
The terminal emulator window provides a means to enter HP-UX commands and the ability to cut and paste text between and within windows.
You can select text within one window and copy it to another location within that window, or to another terminal emulator window.
The original text is left in place. if you want to delete it, you must do so manually.
Cutting text
The highlighted text is copied to an internal "clipboard". The text is not removed from your original source.
Pasting text
A copy of the contents of the clipboard is pasted at the location you indicated. You can make additional copies by repeating the above steps.
eval `resize`You can change the size of the window using the frame components. However, applications running within the window may not know about the resizing and act as if the window were the original size.
application [options] &
Example
The following example starts a digital clock from the command line:
xclock -digital &
There are several ways in which you can customize your terminal emulator:
If the value of scrollBar is True, the terminal emulator windows will have scrollbars. If the value is False, they will not have scrollbars.
Example
The following line sets scrollbars in all hpterm windows:
hpterm*scrollBar: TrueThe following line sets scrollbars only for hpterm windows named "localTerminal":
hpterm*localTerminal*scrollBar: True
Using -display option
-display host:display.screenwhere:
You can find these values by typing env, and examining the DISPLAY line.
The terminal emulator is running on your system, but the window shows on another system.
The following starts an hpterm window on the host computer named anna:
hpterm -display anna:0.1 &
Using rlogin
You can use an existing terminal emulator window to log into a remote host. Once the window is acting as a terminal to the remote host, you can run applications there, redirecting the display back to your system if you desire.
For example, the following command logs onto a system named there, runs the client xload, and redirects the display back to your original system. Assume your system is named here.
rlogin there xload -display here:0.0
Using remsh
The remsh command starts a shell on a remote host, performs some client (often starting a terminal emulator on that host), and redirects the display back to your original system if desired. It has the syntax:
remsh remote -n client -display system:display.screenwhere:
For example, the following command runs xload on the remote host named there, and directs output back to your system, here.
remsh there -n /usr/bin/X11/xload -display here:0.0The remsh command is often used when customizing a menu to access other hosts.
Because the hpterm and xterm only emulate a terminal, your control characters might not be what you are used to on a physical terminal. The ttyModes resource allows you to set control characters for you terminal emulator.
By default, Login Manager sets the following control characters.
The "^" character stands for the Ctrl key. So to interrupt an operation in progress, you press Ctrl C.
The syntax for this resource is:
ttyModes: ^C namewhere name is the control, and C is the character. For example, the default value of ttyModes describing the above list is:
ttyModes: erase ^H intr ^C kill ^U start ^Q stop ^S swtch ^@Additional controls are listed in the xterm or hpterm man pages.